Sage has been one of the most popular culinary herbs since ancient times. It adds great flavor to many different dishes, but this herb also holds a lot of healing properties. Plus, when planted in the garden, it attracts beneficial pollinators and prevents harmful pests. The sage plant is hardy and easy to grow, so if you aren’t already growing this garden powerhouse, perhaps this season is the time to begin. Read on for the essential guide to sage, which will give you all the know-how you need to grow, harvest, preserve, and use sage.

Culinary sage or Salvia officinalis is a perennial herb that is native to the Mediterranean. Part of the mint family, sage grows into a bushy plant up to two feet tall and two feet wide.
It has purple, white, or pink flowers and oblong, gray-green leaves that are covered with a fine fuzz. The leaves have a savory, earthy flavor that is especially popular for use with meat and poultry dishes.
Lori’s Green Blessings
This article was reviewed by herbalist Lori Snyder. This is not to be used as personal medical advice; always consult your health care professional for individual concerns.
Here are Lori’s notes on sage:
There are many benefits to sage; a powerful anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, anti-diabetic, antidepressant, anti-tumor, and gastroprotective. I like to infuse sage into honey, add to my mashed squash or potatoes, drink fresh tea, or rub her scent in my hands while taking a break to breathe.
Sage has lots of nutritional value so eat her up and add to fresh tomato sauce or make sage butter. As with any plants or foods check with your health care professional for any contraindications.
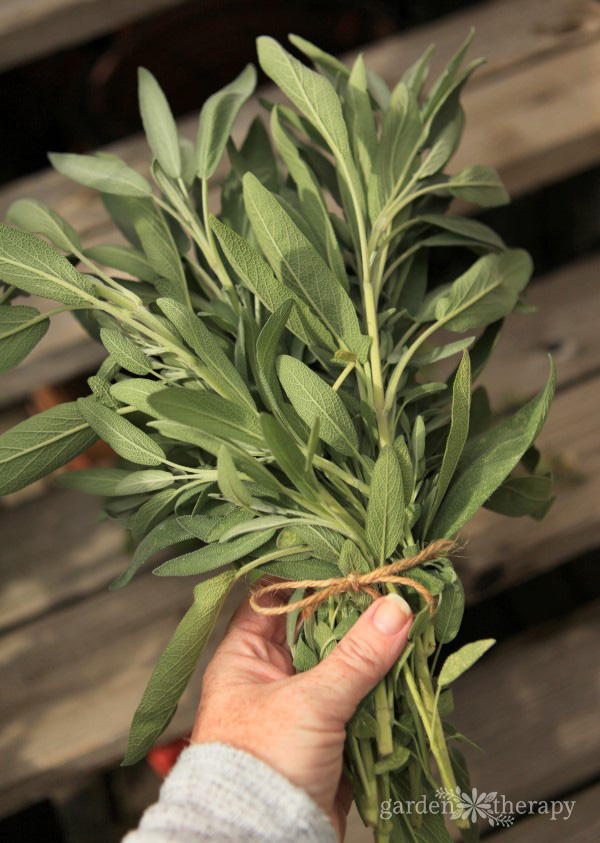

The History of Sage
Sage, like most herbs, has a fascinating history that spans from the Mediterranean to Egypt, to France and China. From boosting fertility to staving off infections, sage has proven its benefits through the ages. Learn more about the history of sage (and a few other herbs) here.
Health Benefits of Sage
The name Salvia comes from the Latin word meaning “to save,” or “to heal,” referring to sage’s ability to heal the body. It has been used medicinally for thousands of years and is still considered a useful healing plant today.
Sage is a powerful anti-inflammatory—when taken internally, it helps to reduce inflammation of the digestive tract, which in turn helps to relieve stomach pains. It is also often used to treat a sore throat, as in this recipe for sage throat lozenges.
Sage also has powerful anti-fungal and antibacterial properties. Ancient Greeks and Romans used sage as a preservative for meat because of its ability to help reduce bacteria.
In aromatherapy, the scent of sage is purported to increase focus and sharpen memory. Try keeping a pot of sage near your desk or workspace and, when you start to feel your focus waning, crush up a leaf and inhale the fragrance.
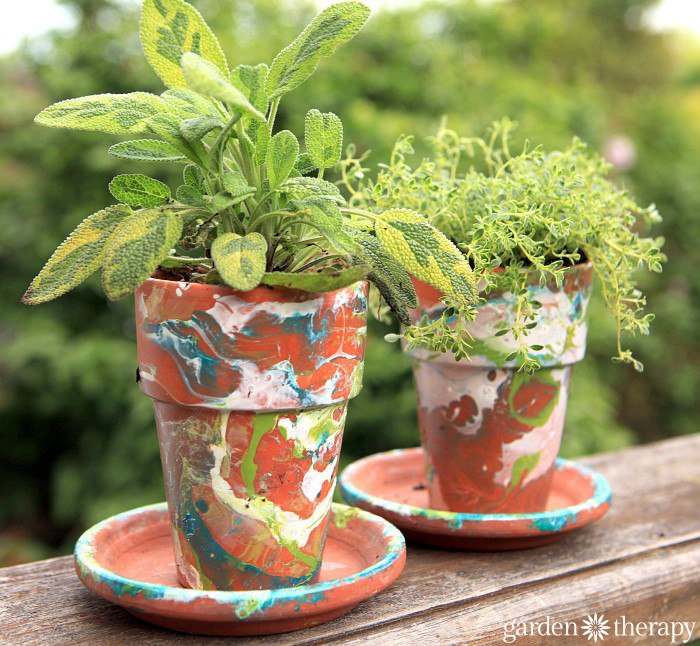

Growing a Sage Plant
Sage is a woody-stemmed, perennial herb in Zones 5-8, and in milder climates, it can be harvested year-round. Common Garden Sage (Salvia officinalis) is a silvery green color and has the best flavor for cooking. There are also many attractive varieties of sage that have purple, variegated, or tricolor leaves.
Sage as a Companion Plant
Sage is a wonderful addition to any garden, both for its herbal and culinary uses and as a garden helper. Even if you don’t cook with sage, consider planting it in your veggie patch as a companion plant to attract beneficial insects and prevent pests. When in bloom, the fragrant flowers attract honeybees and butterflies, while the strong aroma of the leaves helps to deter bean parasites, carrot flies, cabbage maggots, and cabbage flies.
How to Start and Plant Sage
You can start sage indoors from either seed or cuttings. Many people prefer to start it from cuttings because sage is so easy to propagate and taking cuttings will yield large, fully mature plants much quicker than growing from seed.
When planting in the garden, choose a sunny area and give sage plants 25-30” inches of space between each plant so that they have enough room to grow. Plant sage in nitrogen-rich, well-draining soil and water regularly so that it never dries out completely.
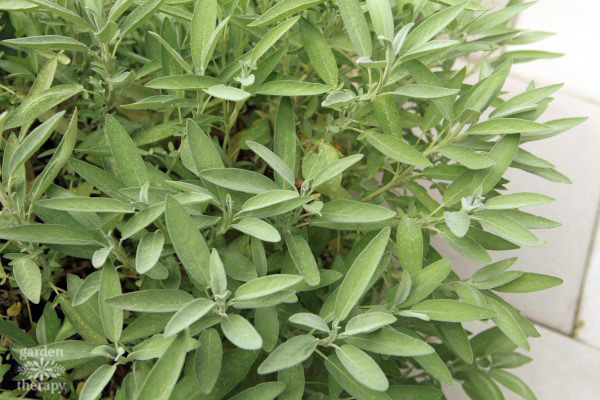

How to Care for a Sage Plant
Prune the plant after its flowering period. Remove any dead wood and cut back the plant to about half its size. This will encourage new growth and your sage plant will stay bushy and neat.
Sage is hardy and overwinters easily. Simply give it some extra mulch in the colder months for protection when the temperatures drop.
Harvesting and Preserving Sage
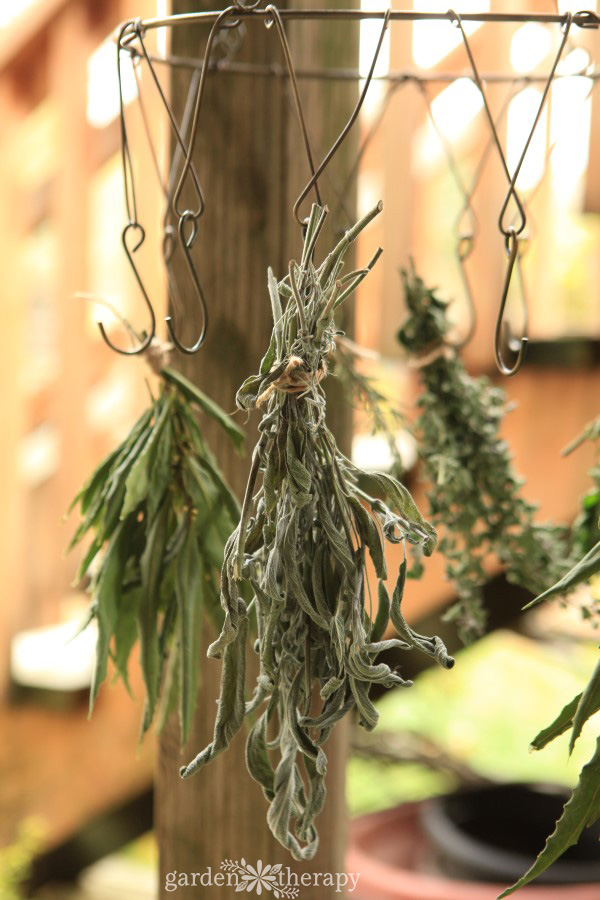

To harvest sage for fresh cooking, remove leaves or stems as needed for recipes. If you need to harvest a large number of leaves, approach it like pruning. Cut stems back to half their size to encourage more bushy growth, or remove full branches from the base to thin out the plant. This will allow you to harvest a large amount of sage while maintaining the shape and health of the plant.
If you have a large harvest or want to dry sage for later use, tie sage stems into bundles and hang upside down in a clean, dry place with good ventilation. When the leaves are fully dried, remove the leaves from the stems (they will crumble into flakes) and store them in an airtight jar. Discard the stems in the compost pile.
What is the Sage Plant Used For?
Use fresh or dried sage leaves in cooking, plant-based beauty recipes, or use it to brew a medicinal tea (you’ll probably want to add a little honey). You can even use it to soothe uncomfortable bug bites—simply crush up a fresh leaf and gently rub the juices onto the affected area.
Plus, try some of these recipe ideas using this herb:
- Add sage to this herbal finishing salt recipe.
- Include a little sage in your favorite poultry stuffing recipe.
- Treat a sore throat with Sage Candy.
- Garnish your favorite cocktail with a fresh sage leaf
- Add fresh or dried sage to simmering spices
You can also use sage as a mosquito deterrent by burning bundles in your campfire, or use it as a helpful tool in fighting against the common cold. As you can see, this plant is versatile and easy to grow, making it a must-have for any home garden.




I am curious if dead sage leaves, that have fallen from the plant, if they still have medicinal properties or values? I know fresh sage leave are invaluable. what about the dead leaves? is there more purpose to them other than compost? any information you can offer will be greatly appreciated. thank you
Hi, no. When the plant leaves have died the constituents are also gone. It’s best to use fresh leaves or healthy dried leaves.
Hi – Thanks so much for this article! I’m wondering if the dried leaves also lose their medicinal properties just like leaves that die naturally. Would it be the same? I’m interested in sage for flavor in food but also for medicinal tea.
I live in 10b and my large common Sage plant has mealybugs on it all over. What is the best way to help my plant? I’ve moved it to mostly shade now and it is isolated from other plants and herbs. Yes I know of the qtip w alcohol trick, but I have more than I can even think of….. Do I neam my plant?